ER Tablets: Extended-Release Medications Explained
When you take an ER tablet, an extended-release medication designed to release its active ingredient gradually over several hours. Also known as controlled-release, it helps keep drug levels stable in your blood instead of spiking and crashing like regular pills. This isn’t just convenience—it’s about safety, consistency, and fewer side effects. If you’ve ever wondered why some pills are bigger, why you can’t crush them, or why your doctor switched you from a twice-daily dose to once-a-day, the answer starts with how your body absorbs medicine over time.
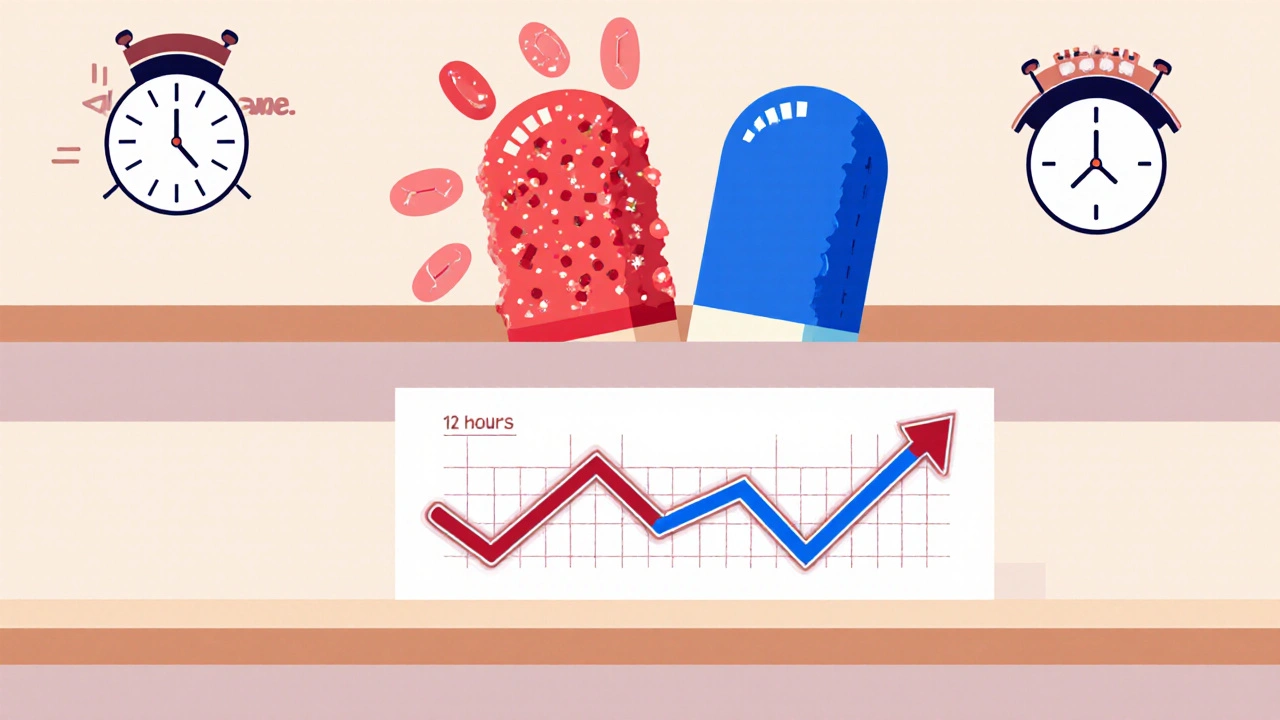
ER tablets work by using special coatings or matrices that slow down how fast the drug dissolves. Think of it like a time-release capsule inside a pill—instead of dumping all the medicine at once, it lets it drip out slowly. This matters most for drugs that need steady levels to work right: blood pressure meds like ER tablets of amlodipine, painkillers like oxycodone ER, or even ADHD drugs like methylphenidate ER. If the drug hits too hard too fast, you get side effects. If it fades too soon, your symptoms come back. ER tablets fix that balance. And because they reduce how often you need to take a pill, they make it easier to stick to your treatment.
Not all extended-release formulas are the same. Some use wax-based cores, others use polymer shells or osmotic pumps. That’s why you can’t split or chew them—breaking the coating ruins the timing. You might also see labels like XR, SR, or CR—those are just different names for the same idea: slow release. And while ER tablets are common for chronic conditions, they’re not always the best fit. For example, if you need fast relief during a migraine or sudden pain, an immediate-release pill works better. But for daily management—whether it’s arthritis, hypertension, or depression—ER tablets give you more control without the rollercoaster.
What you’ll find below are real, practical guides from people who’ve lived with these meds. You’ll read about how ER tablets interact with other drugs, why timing matters when you take them, and how they compare to alternatives. There’s also advice on managing side effects, what to do if you miss a dose, and how insurance handles these formulations. These aren’t theory pieces—they’re from real patients and doctors who’ve seen what works and what doesn’t. Whether you’re new to ER tablets or have been taking them for years, this collection gives you the clear, no-fluff facts you need to stay on track.
Modified-Release Formulations: Key Bioequivalence Rules You Need to Know
Modified-release formulations require specialized bioequivalence testing beyond standard AUC and Cmax. Learn why some generics fail in real-world use, how regulators test them, and what patients should watch for.